
If the world continues to depend on fossil fuels, and their use continues to grow particularly with the emerging and developing countries of the world, technological solutions will be the world’s best chance to achieve decarbonization.
This will require nations to work together and industries to cooperate in order to develop and implement innovative technologies that will help us achieve this goal. Throughout the world, the vast majority of anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions come from the combustion of fossil fuels. There are many sources of greenhouse gas emissions, but the primary sources are electricity and heat production, transportation, agriculture, and manufacturing. Transportation accounts for approximately 15% of global greenhouse gas emission and about 29% of total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, making it the largest contributor of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions. At current greenhouse gas emission rates, temperatures will continue to increase and weather patterns continue to change making it vitally important that something be done, or irreversible damage will occur.
The rise of electrical vehicles (EVs) has gained significant momentum and publicity in recent years both due to their efficient use of energy and positive effect on the environment. Most, if not all of the major car manufacturers are fully committed to the EV race and developing their own line of EVs while some manufactures even plan to go all electric, at least for cars, in the next decade or so. However, despite all of the benefits and potential of EV technology, there are still some forms of transportation that are not suitable for electrification. Heavy-load and long-distance shipping and transportation are not suitable to go electric due to the limitations of current battery technology. This means that the aviation, cargo shipping, and road haulage industries will not be a part of the EV revolution and will still continue to burn fossil fuels and emit carbon dioxide and greenhouse gasses. Therefore, other solutions will be needed if we plan to reduce our emissions across the board. One such example, is carbon-neutral fuel which produces no net-greenhouse gas emissions or carbon footprint.
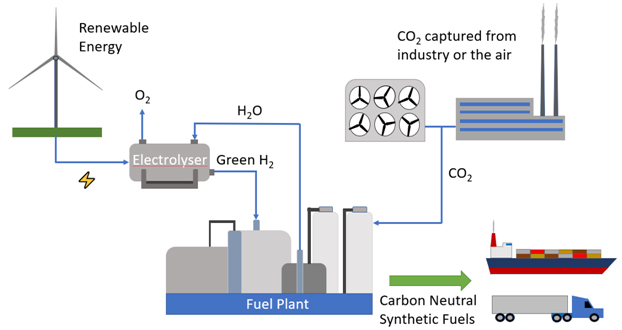
Carbon neutral synthetic fuels capture carbon dioxide in the manufacturing process and use it in chemical reactions with hydrogen to produce synthetic hydrocarbons such as gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and natural gas. The carbon dioxide can be captured from the air or from industrial processes through carbon capture technologies. To be a truly carbon neutral source, the hydrogen is created by electrolysis using renewable energy. Traditional process such as the gasification of coal can be used to produce hydrogen however this would require the use of carbon capture technologies to make it carbon neutral but would still not qualify it as renewable. The hydrogen and carbon dioxide are combined and reacted in the presence of a catalyst to improve the efficiency of the reaction and produce the desired output of hydrocarbon fuels. The synthetic fuels are then sold to the market and can be used in existing engines of cars, trucks, ships, and airplanes for zero net emissions. The overall process is illustrated in Figure 1 shown below.
Synthetic fuels offer some critical advantages over traditional fossil fuels. The most obvious, as we have discussed, is the carbon neutral aspect as these synthetic fuels can help us reduce our global emissions and mitigate the damage that has been and will continue to be done by harmful greenhouse gasses. Another important advantage is that synthetic fuels are cleaner than petroleum fuels as they emit fewer nitrogen oxides and other particles when burned. For example, the heavy metal and sulfur contaminants that are in petroleum fuels can be captured in the production process of synthetic fuels making them more environmentally friendly. Synthetic fuels are also a renewable source of energy and do not require the use of our limited fossil fuels. Lastly, synthetic fuels will work with current internal combustion engine technology and therefore can take advantage of our existing transportation network and established fuel infrastructure for storage and distribution.
There are some drawbacks to carbon neutral synthetic fuels that hinder their large-scale commercial production and subsequent use. Carbon neutral synthetic fuels are currently much more expensive than their petroleum produced equivalent at about five times the cost. There is potential to reduce the cost through innovation and development which will occur over the coming years and decades. The other issue is that the processes necessary to create synthetic fuels, hydrogen production through electrolysis and carbon capture technology, are energy intensive and expensive.
As a short-term solution, one possible way to bring down the cost of synthetic fuels is to use blue hydrogen. As previously explained, the preferred hydrogen production process is through electrolysis using renewable energy. This is known as green hydrogen and is the cleanest hydrogen production process but also the most expensive. Blue hydrogen is derived from fossil fuels such as natural gas through the process of steam methane reforming. In blue hydrogen, the carbon dioxide emissions produced from the process are captured and typically stored underground using Carbon Capture Storage (CCS) technology leaving nearly pure hydrogen. Today, green hydrogen is two to three times more expensive than blue hydrogen, hydrogen produced from fossil fuels in combination with CCS technology. Blue hydrogen also offers another advantage. Since carbon dioxide emissions is captured, it can supplement the carbon dioxide that is captured from the air or other industrial processes and further reduce cost. It is important to maintain the capture of carbon dioxide from the air and external sources as the goal is to be carbon neutral. Blue hydrogen would not qualify the process to be renewable as would the use of green hydrogen, however it is a potential path to consider in helping bring down the cost of carbon neutral synthetic fuels.
Once we have affordable, large-scale production of carbon neutral synthetic fuels, many parts our economy can immediately benefit from them. Long and heavy haul transportation, for all purposes such as travel, shipping, and trade, depend on combustion engines which produce undesirable emissions. EV technology has come a long way but may not be able to help us in all areas. Electric trucks are starting to enter the market to replace diesel for short and medium haul duties however it is still unknown if EVs are feasible for long-distance haulage. Shipping and aviation are a completely different animal. Converting full-size airliners or cargo planes is impractical because of the size and weight of the required battery pack that would be required to power such an aircraft. Cargo ships face a similar problem due to the size and weight of the vessel plus the enormous distances that they travel. There are planned, small electric powered container ships and commercial planes, but these are orders of magnitude smaller and lighter and have less range than their full-size counter counterpart. Therefore, we will still need combustion engines to power these large vessels for the foreseeable future, so carbon neutral synthetic fuels can help reduce or eliminate emissions produced from these industries.
As long as global greenhouse gas emissions continue to increase, we can expect that temperatures will rise, and weather patterns will change having drastic effects on our climate. It becomes increasingly important that we change our way if we want to mitigate these consequences. There is no single solution to this world issue and a combination of solutions may be required to help us reach this goal. Unfortunately for certain industries, the options are limited, and electrification may not be a feasible approach due to the limitation of battery technology. Synthetic fuels may be an important part of the solution in helping us achieve carbon neutrality in industries such as long and heavy haul transportation. These fuels can not only help reduce global emissions but can also be used with our existing transportation network and established fuel infrastructure making it a more adaptable technology. As we may be able to adapt various sectors of our transportation network to rely on EV technology such as public and private transportation, developing countries may not have the resources or same motivation to replace their existing vehicles and infrastructure so synthetic fuels can be a great asset to those places. Carbon neutral synthetic fuels offer many advantages and should be seriously considered as a solution to our climate change crisis.
